Add to Cart
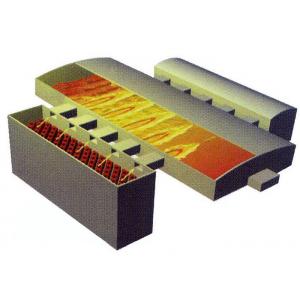
Dual Fuel Combustion , Glass Melting Furnace, Cross Fired Furance
1. Brief Introduction
Glass is a special amorphous inorganic nonmetallic material. The main component is silicate, a non-crystalline solid with an irregular structure.
Glass was used for windows and doors by the Ancient Romans as early as the 4th century.
Glass melting is a very complex process, it includes physical, chemical and physicochemical phenomena and reaction. These phenomena and reaction lead the mechanical mixed raw materials to complex melting glass liquid.
The direction of flames of a cross fired furnace is from one side to the other side, which is across the width of the furnace and perpendicular with the flow direction of glass liquid.

2. Factors that influence the melting effects
| 1 | Characteristic of raw materials |
| 2 | Chemical compon |
| 3 | Material feeding method |
| 4 | Melting temperature |
3. Process
| 1 | The batching materials go into the furnace |
| 2 | The solid materials melt into glass liquid |
| 3 | The glass liquid goes into throat after clearing, homogenization and cooling. |
4. Main component
The melting tank is combined with melting area and clearing area.
The regenerator as a waste heat recovery device, the combustion air flows through the regenerator, after preheated, it will arrive at the furnace through the port.
It is the place where the fuel is mixed with the preheated air, also an access for the preheated air in to the furnace and exhausting the
waste gas out.
The dimension of batch charging area is determined by the different size of furnace and batching methods.
Throat is a core section of the furnace, it will affect the quality of glass and furnace campaign. The temperature of glass will reduce when flowing through the throat.